ISA 101 writeup
Challenge description
Goal of the challange is to reverse engineer code written in ISA (documentation) - assembly language designed by Black Bauhinia.
With challange we get 2 urls:
Challenge: https://c58a-ish-1.hkcert24.pwnable.hk?id=3
Playground: https://c58b-ish-2.hkcert24.pwnable.hk?id=1
We can access the executable and download assembly in the challenge url, and the playground url is a web interface to run and debug the ISA code.
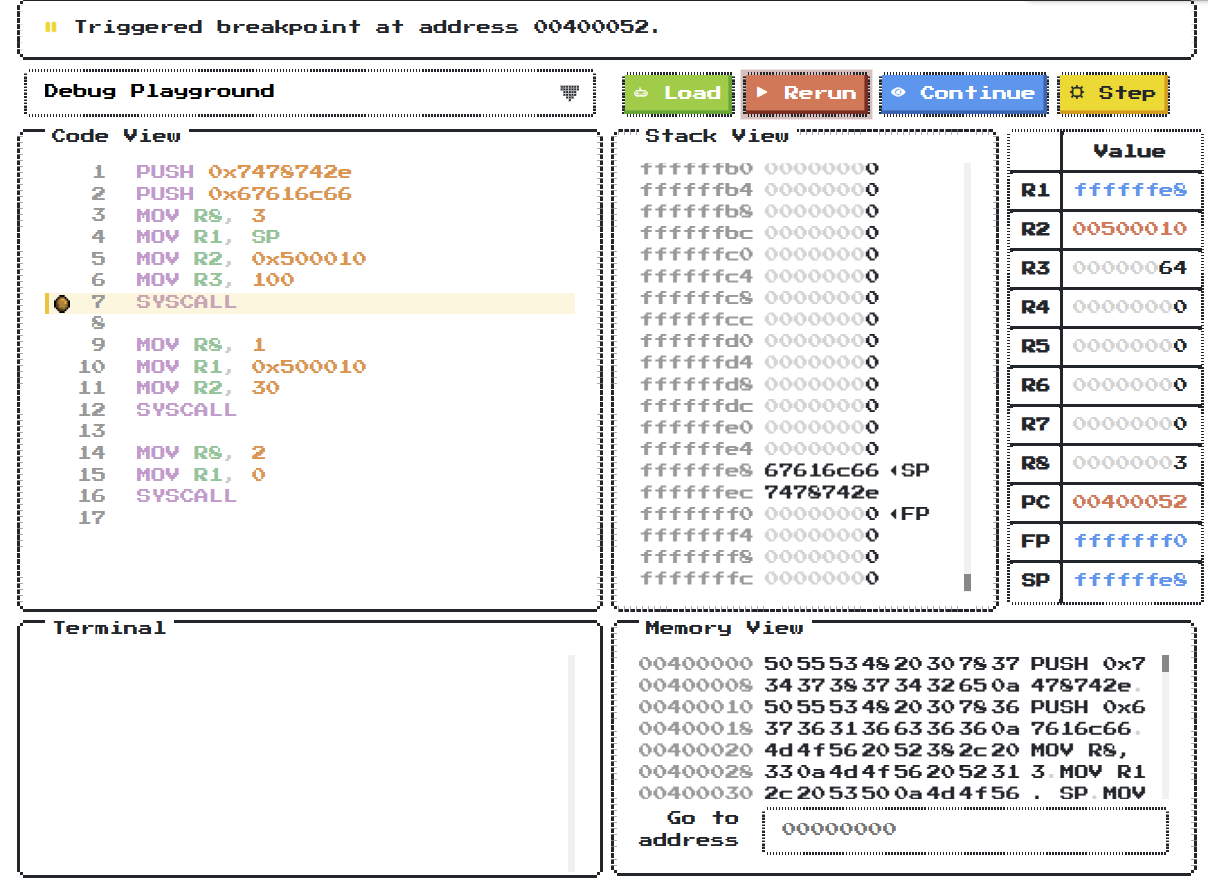
Solution
Assembly code (with added comments):
JMP 0x400088;
PUSH FP;
MOV FP, SP;
SUB SP, 4;
MOV R1, [FP+8];
MOV R8, 5;
SYSCALL;
MOV R2, R1;
MOV R1, 0;
MOV SP, FP;
POP FP;
RET;
SUB SP, 364;
MOV R1, SP;
MOV SP, FP;
SUB SP, 0;
PUSH 0xb146f66e; //xor keys pushed on stack
PUSH 0x2fd8b7c1;
PUSH 0x95e11585;
PUSH 0xcf39fb28;
PUSH 0xb3accf4c;
PUSH 0xdb22a8cb;
PUSH 0xe21f60cd;
PUSH 0xb660d0fe;
PUSH 0x8be89ec9;
PUSH 0x241bd185;
PUSH 0x161d7e99;
PUSH 0xbf3a7f64;
PUSH 0xea7454ee;
PUSH 0x2e04ce47;
PUSH 0x18b25e16;
PUSH 0x2295643e;
PUSH 0x49f8d91f;
PUSH 0x3f541ea6;
PUSH 0x113d8a6f;
PUSH 0x38726ccc;
PUSH 0x2e27be68;
PUSH 0xd4e398ea;
PUSH 0x7fcba040;
PUSH 0xeec775f5;
PUSH 0x478ff266;
PUSH 0x718a3507;
PUSH 0x536edeba;
PUSH 0xf0efb119;
PUSH 0x9efdd1c2;
PUSH 0x977b4203;
PUSH 0x2ceeda0d;
PUSH 0xfdc086ff;
PUSH 0x2303c15a;
PUSH 0x3c9d30a1;
PUSH 0x193f231b;
PUSH 0x1a06a63f;
PUSH 0x5c829f5;
PUSH 0x49c872b8;
PUSH 0x92bcbdad;
PUSH 0xa9a5a84e;
PUSH 0xb16969c;
PUSH 0xb58b3659;
PUSH 0x642069c9;
PUSH 0x9c37ba69;
PUSH 0x623277a4;
PUSH 0x17b6f65c;
PUSH 0xa6a21506;
PUSH 0x15881c76;
PUSH 0x96ed9c50;
PUSH 0x21226b56;
PUSH 0xd8890218;
PUSH 0xca6eddde;
PUSH 0x9a18e395;
PUSH 0x936f6277;
PUSH 0xaf23d230;
PUSH 0x88d9666a;
PUSH 0xff591d2f;
PUSH 0xce454872;
PUSH 0xf3391e9f;
PUSH 0x4ddd147f;
PUSH 0x404bcc99;
PUSH 0x5becacfd;
PUSH 0x1d9f2f1;
PUSH 0xc833a241;
MOV SP, R1;
MOV R1, FP;
SUB R1, 356;
MOV R2, 100;
MOV R8, 0;
SYSCALL; //read input
MOV R2, R8;
MOV R3, 0;
MOV R4, FP;
SUB R4, 256;
MOV R5, R4;
ADD R5, R3;
MOV R6, R1;
ADD R6, R3;
MOV R7, [R5];
XOR [R6], R7; //xor input with key
MOV [FP-360], R2;
MOV [FP-364], R3;
MOV R1, FP;
SUB R1, 356;
MOV R2, [FP-360];
MOV R3, [FP-364];
ADD R3, 4;
LT R3, 100;
JNZ -231; //loop
MOV R4, R1;
ADD R4, R2;
MOV [R4], 0;
MOV R4, R1;
ADD R4, 0;
EQ [R4], 29548; //check if decrypted value begins wth 29548
JNZ +9;
JMP +20;
MOV R8, 4;
SYSCALL;
MOV R4, R1;
ADD R4, 0;
EQ [R4], 1667594341; //check if decrypted value begins wth 1667594341
JNZ +9;
JMP +94;
MOV R4, R1;
ADD R4, 5;
PUSH R4;
MOV [FP-360], R2;
MOV [FP-364], R3;
CALL 0x400014;
ADD SP, 4;
MOV R1, 0;
MOV R8, 2;
SYSCALL;
ADD SP, 364;
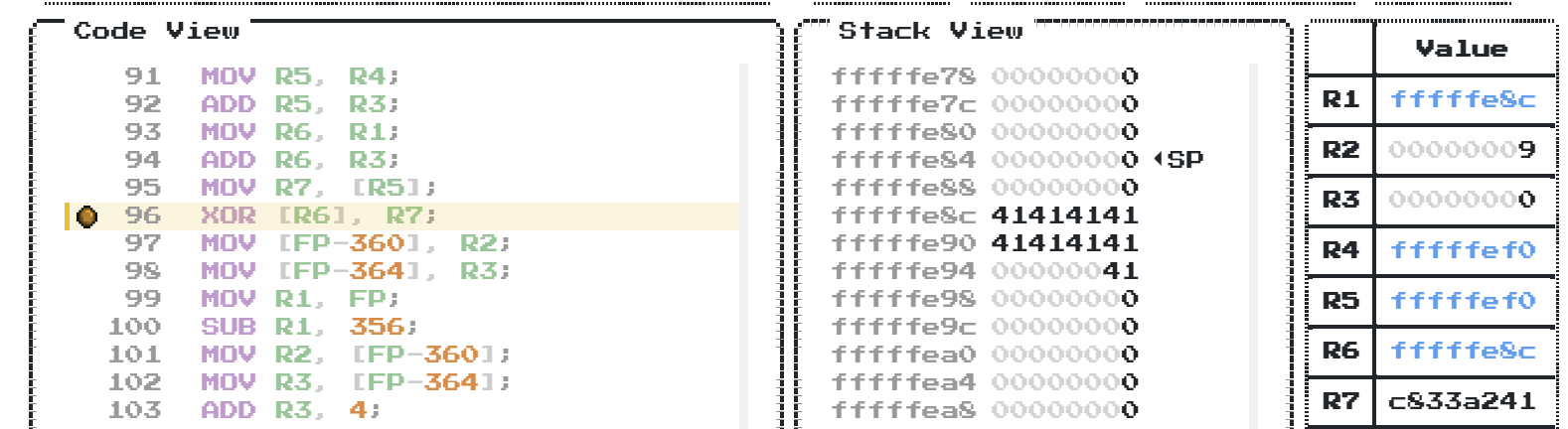
After inspecting the code (adding breakpoints on XOR, and on value checks), we can see that it takes some input from the user (on image 4141… = ‘AAAAA..’), encrypts it (or better said, decrypts it) by xor-ing with values from the stack (stored in R7 register), and then checks if the decrypted value begins with 29548 or 1667594341. Let’s inspect these values:
check1 = 29548
check2 = 1667594341
print(check1.to_bytes(4, byteorder='little').decode('utf-8'))
print(check2.to_bytes(4, byteorder='little').decode('utf-8'))
output:
ls
exec
So the decrypted value should be either “ls” or “exec”. Also from the assembly we can retreive xor keys, so we can encrypt the values “ls” and “exec” and use them as input. (ENDIANSESS IS WORST ENEMY)
def swap_endian(value):
return int.from_bytes(value.to_bytes(4, byteorder='little'), byteorder='big')
xor = [0xc833a241,0x01d9f2f1,0x5becacfd,0x404bcc99,0x4ddd147f,0xf3391e9f]
ls ='ls'
ls = int.from_bytes(ls.encode('utf-8'), byteorder='little')
print(hex(swap_endian(xor[0]^ls))[2:])
output:
2dd133c8
After using 2dd133c8 as input, we get the output:

Now we can use exec to execute the printflag_19876bc2 and get the flag.
exec = 'exec printflag_19876bc2'
exec = int.from_bytes(exec.encode('utf-8'), byteorder='little')
exec = [(exec >> (32 * i)) & 0xFFFFFFFF for i in range((exec.bit_length() + 31) // 32)]
payload = ''
for i in range(6):
payload+=hex(swap_endian(exec[i] ^ xor[i]))[2:]
print(payload)
output:
24da56abd182ab6893d88a37f8ab1471462cea7bfd7d0bf3
And after using 24da56abd182ab6893d88a37f8ab1471462cea7bfd7d0bf3 as input, we get the flag:

hkcert25{x0r_1n_isa_r04d_t0_fullch4in!!!}
Final script:
def swap_endian(value):
return int.from_bytes(value.to_bytes(4, byteorder='little'), byteorder='big')
xor = [0xc833a241,0x01d9f2f1,0x5becacfd,0x404bcc99,0x4ddd147f,0xf3391e9f]
print('decoded')
check1 = 29548
check2 = 1667594341
print(check1.to_bytes(4, byteorder='little').decode('utf-8'))
print(check2.to_bytes(4, byteorder='little').decode('utf-8'))
print('payloads')
ls ='ls'
ls = int.from_bytes(ls.encode('utf-8'), byteorder='little')
print(hex(swap_endian(xor[0]^ls))[2:])
exec = 'exec printflag_19876bc2'
exec = int.from_bytes(exec.encode('utf-8'), byteorder='little')
exec = [(exec >> (32 * i)) & 0xFFFFFFFF for i in range((exec.bit_length() + 31) // 32)]
payload = ''
for i in range(6):
payload+=hex(swap_endian(exec[i] ^ xor[i]))[2:]
print(payload)